 Book Appt.
Book Appt.
 Call Now
Call Now


Paracentesis and thoracentesis are two medical procedures used to remove excess fluid that accumulates in the abdominal and chest cavities, respectively. These procedures are essential for diagnosing and treating various medical conditions that can lead to fluid buildup.
Paracentesis
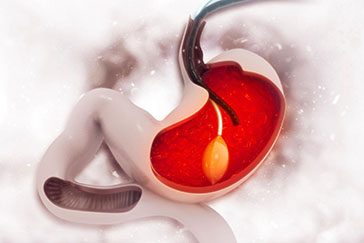
Paracentesis is a medical procedure that involves the removal of excess fluid from the abdominal cavity, a condition known as ascites. Ascites can result from various underlying medical conditions, including liver cirrhosis, heart failure, kidney disease, and certain cancers. The accumulation of fluid in the abdomen can lead to discomfort, pain, difficulty breathing, and other complications.
The Procedure
Thoracentesis
Thoracentesis is a medical procedure performed to remove excess fluid or air from the pleural space, the area between the chest wall and the lungs. This accumulation of fluid, known as pleural effusion, can result from various medical conditions, including pneumonia, heart failure, lung cancer, and tuberculosis. Pleural effusion can cause symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, and coughing.
The Procedure
Potential Risks and Considerations
Both paracentesis and thoracentesis are generally considered safe procedures. However, there are some potential risks and considerations:
Outlook
Paracentesis and thoracentesis are essential medical procedures used to remove excess fluid or air from the abdominal and chest cavities, respectively. These procedures play a crucial role in diagnosing and managing various medical conditions associated with fluid buildup. While they are generally safe and well-tolerated, they require careful monitoring and skilled healthcare providers to minimize potential risks. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms related to abdominal or chest fluid accumulation, it is essential to seek prompt medical attention for evaluation and potential treatment through paracentesis or thoracentesis, as appropriate to the specific condition.
SHALBY Sanar International Hospitals provides extensive medical procedures backed up with our state-of-the-art technology and a team of highly qualified & experienced clinical experts.

Acute Gastroenteritis Treatment by Dr. Amit Mittal | SHALBY Sanar International Hospitals
Our doctors pen down their research findings and experiences from time to time. Their words provide deep insight into the latest techniques, technologies and other advancements in healthcare. It provides expert answers to all kinds of health questions for real-life issues.
VIEW ALL

Since the day of its foundation, SHALBY Sanar International Hospitals is committed to provide comprehensive healthcare services. It regularly organizes awareness programs in its premises and encourages outdoor healthcare activities and camps with an intent to put focus on preventive healthcare.
VIEW ALL