 Book Appt.
Book Appt.
 Call Now
Call Now


Introduction
Hip replacement is a surgical operation. An orthopaedic surgeon will replace your hip (or sections of it) with a man-made implant (prosthesis). Your surgeon may refer to a hip replacement as a hip arthroplasty. Surgeons execute more than 90% of hip replacements on persons over the age of fifty. If pain and other hip symptoms interfere with your ability to stand, walk, and move, your specialist may prescribe a hip replacement. Your surgeon will perform one of two types of hip replacements: total hip replacement or partial hip replacement.
When will I need a hip replacement?
If problems in your hip make it difficult (or impossible) to participate in your normal activities, you may be an excellent candidate for a hip replacement. Most people who undergo hip replacement surgery first try other, more conservative treatments such as medicine, physical therapy, or the use of a cane or walker. Your doctor will most likely propose these types of therapies before recommending a hip replacement.
Arthritis is the most common cause of hip pain and other problems that require a hip replacement. Osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and psoriatic arthritis are among the most prevalent kinds of arthritis that can affect the hip.
Other health diseases and difficulties that can cause hip joint degeneration and necessitate a hip replacement include osteonecrosis, traumas such as automobile accidents or falls, femoroacetabular impingement syndrome (FAI or hip impingement), hip dysplasia, benign tumours (neoplasms), cancer, and Perthes disease.
Procedure Details
Before procedure
Before your hip replacement surgery, your surgeon will do a physical examination and testing. They will enquire about your symptoms and assess your existing range of motion (how far you can move your hip). Inform your surgeon about any medications or supplements you are currently using. Your surgeon will compare the hip you're replacing with your other hip. They will ask you to move your hips in various directions. These steps will allow them to assess the muscles that support your hip and leg.
Before a hip replacement, you will most likely need multiple tests, including hip X-rays, blood tests such as a basic metabolic panel (BMP), and urinalysis (a urine test). X-rays may not be the only imaging examination required. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography (CT) scans, and electrocardiograms (EKG) are all possible orders from your surgeon.
During procedure
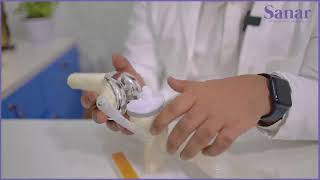
During a hip replacement, your surgeon will remove part or all of your hip and replace it with a prosthetic. You will be given regional anesthesia before your surgery. Regional anesthesia relieves pain in a big area of your body without entirely putting you to sleep. Some providers call regional anesthesia a spinal or a spinal block. Whatever form of hip replacement you require, your surgeon will remove bone and cartilage from your current hip joint and replace it with a prosthesis. Prosthetic hips are often composed of metal, plastic, or ceramic.
After procedure
Most hip replacement surgeries are outpatient, so you can go home the same day. You may have to stay in the hospital overnight (outpatient extended recovery). Your anesthesiologist will make certain that you wake up well after anesthesia and that there are no immediate complications from your procedure.
Benefits
Hip replacements are typically highly successful operations. Most people who get hip replacement enjoy a significant reduction in their symptoms, particularly pain and stiffness. When you've fully recovered, you should have more mobility and range of motion in your hip. A hip replacement typically makes it simpler to walk, climb stairs, and engage in other physical activity.
Risks
Hip replacement complications are rare, although they can occur. The most common risks are infections, blood clots in your legs (deep vein thrombosis) or lungs (pulmonary embolism), prosthesis issues such as loosening or dislocating, bone fractures (broken bones) around the prosthesis, and joint stiffness.
Conclusion
Total hip replacement surgery is a highly effective technique to reduce chronic hip discomfort and increase mobility in individuals who have had considerable joint degeneration as a result of diseases such as arthritis, fractures, or avascular necrosis. Patients can recover their range of motion and quality of life by replacing their injured hip joint with a prosthetic implant. While the operation is generally safe, it does have hazards such as infection, blood clots, and implant loosening, which can be reduced with correct surgical methods, post-operative care, and rehabilitation. To provide the best possible results, recovery usually includes a combination of pain treatment, physical therapy, and follow-up monitoring.
SHALBY Sanar International Hospitals provides extensive medical procedures backed up with our state-of-the-art technology and a team of highly qualified & experienced clinical experts.



Life Transformed: Mr. Blojah Felix Journey to Pain-Free Living | SHALBY Sanar

Pain-Free Living After 6 Years: Knee Replacement Success Story | Dr. Rohit Lamba

Bilateral Total Knee Replacement by Dr. Vikram Shah | SHALBY Sanar International Hospitals

Remarkable Recovery Story: Hip Replacement for Non-union Fracture

Incredible Recovery Story: Bilateral Knee Replacement Transformation

Knee Replacement Surgery by Dr. Rohit Lamba: 60-Year-Old's Remarkable Recovery

Renewed Hope: Successful Hip Replacement Surgery Transforms Iraqi Patient's Life

Exploring a Case of Revision Knee Replacement: Insights from Dr. Rohit Lamba
Triumphant Journey: Ms. Fatima, 69, Triumphs Over Revision Knee Replacement Surgery

Leaving the crutches behind – Riyaz, 43, gains confidence after a successful Hip Replacement Surgery

Transformative Total Knee Replacement Surgery: A New Lease on Life for 48-Year-Old Ramesh

Miraculous Recovery: 17-Year-Old Kenyan Overcomes Osteosarcoma with Mega Prosthesis Surgery

Mr. Omar Faruk's Remarkable Knee Recovery: ACL Reconstruction Success Story

Mrs. Vijay Luxmi's Remarkable Knee Replacement Journey

Umidjon, 36, from Uzbekistan shares his gratitude for a successful total hip replacement surgery
Ms. Mohsin from Iraq shares her gratitude for a successful Computer Navigated Total Knee Replacement

A Total Hip Replacement surgery gives Ms. Barry from Ghana, the ability to walk again.

Dr. Rohit Lamba talks about a successful Hip Replacement Surgery carried out on an Iraqi patient
Our doctors pen down their research findings and experiences from time to time. Their words provide deep insight into the latest techniques, technologies and other advancements in healthcare. It provides expert answers to all kinds of health questions for real-life issues.
VIEW ALL.png)
.png)


Since the day of its foundation, SHALBY Sanar International Hospitals is committed to provide comprehensive healthcare services. It regularly organizes awareness programs in its premises and encourages outdoor healthcare activities and camps with an intent to put focus on preventive healthcare.
VIEW ALL