 Book Appt.
Book Appt.
 Call Now
Call Now


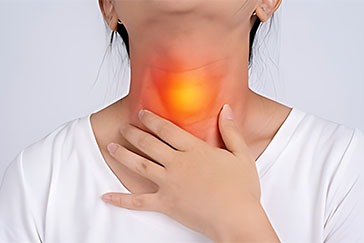
The thyroid gland, a small butterfly-shaped organ located in the neck, plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions. It produces hormones that influence metabolism, growth, development, and overall energy balance. When the thyroid gland malfunctions, it can lead to a range of disorders, both hyperactive and underactive, affecting millions of people worldwide.
Thyroid Gland Functions
The thyroid gland produces two main hormones, thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which are critical for maintaining metabolic processes and overall health. These hormones influence:
Common Thyroid Disorders
Hypothyroidism
Causes: Hypothyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones. The most common cause is autoimmune thyroiditis, also known as Hashimoto's thyroiditis. Other causes include thyroid surgery, radiation therapy, certain medications, and congenital factors.
Symptoms: Symptoms of hypothyroidism may include fatigue, weight gain, cold intolerance, depression, constipation, dry skin, and muscle weakness.
Diagnosis: Blood tests measuring thyroid hormone levels (TSH, T4, and T3) can diagnose hypothyroidism.
Treatment: Hypothyroidism is typically managed by taking synthetic thyroid hormone medication, such as levothyroxine, to restore normal hormone levels.
Hyperthyroidism:
Causes: Hyperthyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland produces an excessive amount of thyroid hormones. The most common cause is Graves' disease, an autoimmune disorder. Other causes may include thyroid nodules, thyroiditis, or excessive iodine intake.
Symptoms: Symptoms of hyperthyroidism may include rapid heartbeat, weight loss, anxiety, heat intolerance, sweating, and hand tremors.
Diagnosis: Blood tests measuring thyroid hormone levels, along with imaging studies like a thyroid scan or ultrasound, can diagnose hyperthyroidism.
Treatment: Treatment options include medications to reduce thyroid hormone production, radioactive iodine therapy to shrink the thyroid gland, or surgery to remove part or all of the gland.
Thyroid Nodules:
Causes: Thyroid nodules are growths or lumps that form within the thyroid gland. They can be benign (noncancerous) or malignant (cancerous). The exact cause of thyroid nodules is often unknown.
Symptoms: Most thyroid nodules do not cause symptoms and are discovered incidentally during a physical examination or imaging study. However, some larger nodules may cause neck pain, difficulty swallowing, or voice changes.
Diagnosis: Nodules are typically evaluated through ultrasound imaging and fine-needle aspiration biopsy to determine if they are cancerous or benign.
Treatment: Treatment depends on the nature of the nodule. Benign nodules may be monitored or surgically removed if they cause symptoms. Malignant nodules require surgery, radiation, and potentially other treatments.
Thyroiditis:
Causes: Thyroiditis refers to inflammation of the thyroid gland, which can be caused by various factors, including viral infections, autoimmune disorders, or medications.
Symptoms: Symptoms can vary depending on the type of thyroiditis but may include neck pain, fever, fatigue, and changes in thyroid hormone levels.
Diagnosis: Blood tests, imaging studies, and thyroid function tests can help diagnose thyroiditis.
Treatment: Treatment depends on the underlying cause and type of thyroiditis. Management may include anti-inflammatory medications or hormone therapy.
Outlook
The thyroid gland is a small but vital organ that regulates numerous physiological processes in the body through the production of thyroid hormones. When the thyroid gland malfunctions, it can lead to a range of disorders, including hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, thyroid nodules, and thyroiditis. Prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment are essential for managing these thyroid disorders effectively and maintaining overall health. If you suspect you have a thyroid disorder or experience symptoms related to thyroid dysfunction, it is crucial to seek medical evaluation and guidance from a healthcare professional. Thyroid disorders are manageable, and with proper care, individuals with these conditions can lead healthy and fulfilling lives.
SHALBY Sanar International Hospitals provides extensive medical procedures backed up with our state-of-the-art technology and a team of highly qualified & experienced clinical experts.

Patient from Zimbabwe Treated by Dr. (Prof) Amit Kumar Sharma | SHALBY Sanar International Hospitals

Sudan’s Yiel Hoal Wei Regains Hearing with BAHA Surgery | Dr. Amit Kumar Sharma
Our doctors pen down their research findings and experiences from time to time. Their words provide deep insight into the latest techniques, technologies and other advancements in healthcare. It provides expert answers to all kinds of health questions for real-life issues.
VIEW ALL

Since the day of its foundation, SHALBY Sanar International Hospitals is committed to provide comprehensive healthcare services. It regularly organizes awareness programs in its premises and encourages outdoor healthcare activities and camps with an intent to put focus on preventive healthcare.
VIEW ALL