 Book Appt.
Book Appt.
 Call Now
Call Now


Muscular Dystrophy (MD) is a group of genetic disorders characterized by progressive muscle weakness and degeneration. It primarily affects the skeletal muscles responsible for movement, and in some forms, cardiac and respiratory muscles may also be affected. Muscular Dystrophy is caused by mutations in genes responsible for producing proteins essential for muscle function.
Types of Muscular Dystrophy:
Symptoms of Muscular Dystrophy:
The symptoms of Muscular Dystrophy can vary widely depending on the specific type and its progression. Common signs include:
Diagnosis:
Diagnosing MD involves a combination of clinical evaluation, genetic testing, muscle biopsies, and electromyography (EMG) to assess electrical activity in muscles. Genetic testing is particularly crucial for identifying specific gene mutations associated with different forms of MD.
Treatment and Management:
While there is currently no cure for Muscular Dystrophy, management strategies focus on improving quality of life, maintaining mobility, and managing symptoms. These may include:
Ongoing research in the field of Muscular Dystrophy aims to develop targeted therapies, including gene therapy and gene-editing techniques. Clinical trials are underway to test potential treatments that hold promise for modifying the course of the disease.
In conclusion, Muscular Dystrophy encompasses a group of genetic disorders that result in progressive muscle weakness and degeneration. While it presents significant challenges, advances in medical research and interventions offer hope for improved management and potentially curative treatments in the future. Through comprehensive care, support, and ongoing research efforts, the goal remains to enhance the lives of individuals affected by this complex condition.
SHALBY Sanar International Hospitals provides extensive medical procedures backed up with our state-of-the-art technology and a team of highly qualified & experienced clinical experts.

Patient from Iraq gets treated by Dr. Harnarayan Singh | SHALBY Sanar International Hospitals

15 year old Patient from Liberia gets treated by Dr Harnarayan Singh | Neurosurgery & Spine Surgery

Mrs. Khalida Khaleel from Iraq Overcomes Degenerative Disc & Grade 1 Spondylolisthesis

Successful Treatment of a Patient from Uzbekistan for Degenerative Disc Disease and Back Syndrome

Surviving Stroke: Bipasha Banerjee's Testimony on Timely Intervention
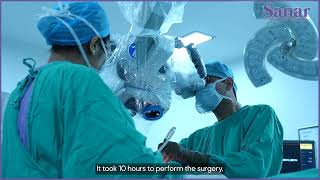
Successful Intraoperation Neuro Monitoring on patient Hasan from Iraq
Successful removal of Glioma using advanced machines

A multidisciplinary care worked wonders for Ms. Akhtamova from Tajikistan
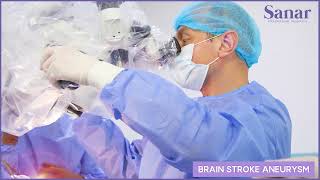
Treatment for Brain Aneurysm - Al Qumairi Saeed Mohsen Awadh from Yemen
Our doctors pen down their research findings and experiences from time to time. Their words provide deep insight into the latest techniques, technologies and other advancements in healthcare. It provides expert answers to all kinds of health questions for real-life issues.
VIEW ALL


Since the day of its foundation, SHALBY Sanar International Hospitals is committed to provide comprehensive healthcare services. It regularly organizes awareness programs in its premises and encourages outdoor healthcare activities and camps with an intent to put focus on preventive healthcare.
VIEW ALL