 Book Appt.
Book Appt.
 Call Now
Call Now


Lumbar Disc Disease, commonly referred to as Herniated Disc, is a prevalent spinal condition that affects the lower back. It occurs when the soft, gel-like material within a spinal disc protrudes or leaks out, pressing against nearby nerves. This can lead to a range of symptoms and discomfort.
Understanding Lumbar Disc Disease begins with comprehending the spinal structure. The spine, or vertebral column, is comprised of a series of bones called vertebrae. Between each vertebra lies an intervertebral disc—a flexible structure that acts as a shock absorber and allows for movement. Each disc is composed of an outer layer (annulus fibrosus) and an inner gel-like core (nucleus pulposus).
Causes of Lumbar Disc Disease:
Lumbar Disc Disease can result from various factors, including:
Symptoms:
Diagnostic Methods:
Treatment Options:
In conclusion, Lumbar Disc Disease, or Herniated Disc, is a common condition affecting the lower back due to protrusion of spinal disc material. With proper diagnosis and a comprehensive treatment plan, individuals can manage symptoms and regain their quality of life. Additionally, lifestyle adjustments and preventive measures can contribute to long-term spine health. It's essential to consult a healthcare professional for personalized guidance and care.
SHALBY Sanar International Hospitals provides extensive medical procedures backed up with our state-of-the-art technology and a team of highly qualified & experienced clinical experts.

Patient from Iraq gets treated by Dr. Harnarayan Singh | SHALBY Sanar International Hospitals

15 year old Patient from Liberia gets treated by Dr Harnarayan Singh | Neurosurgery & Spine Surgery

Mrs. Khalida Khaleel from Iraq Overcomes Degenerative Disc & Grade 1 Spondylolisthesis

Successful Treatment of a Patient from Uzbekistan for Degenerative Disc Disease and Back Syndrome

Surviving Stroke: Bipasha Banerjee's Testimony on Timely Intervention
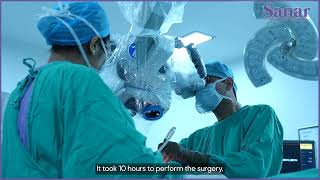
Successful Intraoperation Neuro Monitoring on patient Hasan from Iraq
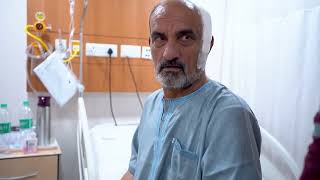
Successful removal of Glioma using advanced machines

A multidisciplinary care worked wonders for Ms. Akhtamova from Tajikistan
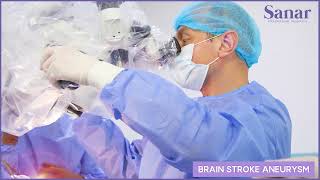
Treatment for Brain Aneurysm - Al Qumairi Saeed Mohsen Awadh from Yemen
Our doctors pen down their research findings and experiences from time to time. Their words provide deep insight into the latest techniques, technologies and other advancements in healthcare. It provides expert answers to all kinds of health questions for real-life issues.
VIEW ALL


Since the day of its foundation, SHALBY Sanar International Hospitals is committed to provide comprehensive healthcare services. It regularly organizes awareness programs in its premises and encourages outdoor healthcare activities and camps with an intent to put focus on preventive healthcare.
VIEW ALL