 Book Appt.
Book Appt.
 Call Now
Call Now


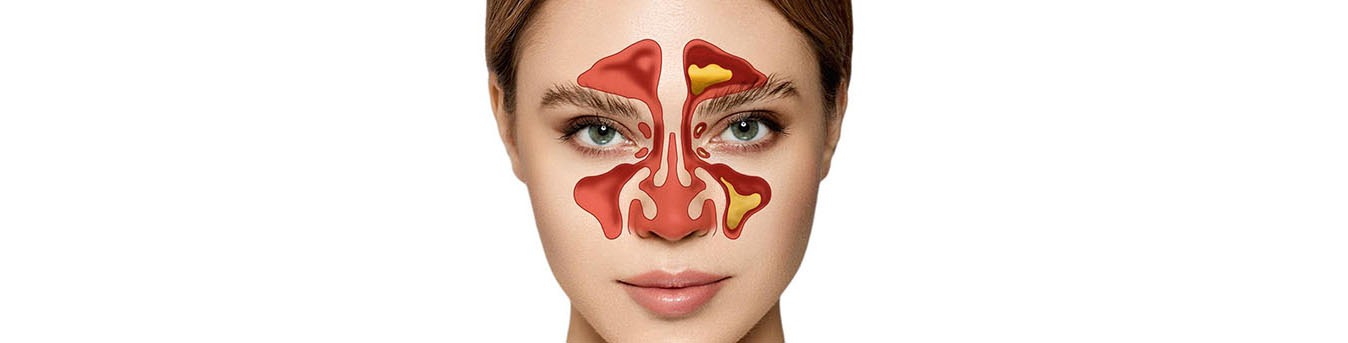
Sinusitis, commonly known as a sinus infection, is a condition characterized by inflammation and swelling of the sinuses, which are air-filled spaces within the facial bones. It can cause discomfort, facial pain, congestion, and other symptoms that can significantly impact daily life. While various factors contribute to the development of sinusitis, understanding and managing its triggers are key to both prevention and effective treatment.
Identification of Triggers:
Allergens: Allergies to pollen, dust mites, mold, and pet dander can trigger sinusitis symptoms. Identifying and avoiding these allergens can help prevent recurrent sinus infections. Allergy testing conducted by an allergist can pinpoint specific triggers, enabling targeted avoidance strategies.
Environmental Irritants: Exposure to irritants such as cigarette smoke, strong odour’s, and pollution can inflame the sinuses and exacerbate sinusitis. Minimizing exposure to these irritants, especially in enclosed spaces, can help reduce the risk of sinusitis.
Viral Infections: Sinusitis often follows a viral upper respiratory infection, such as a cold or flu. Practicing good hygiene, such as regular handwashing and avoiding close contact with sick individuals, can reduce the likelihood of viral infections that can lead to sinusitis.
Bacterial Infections: Bacterial sinus infections can occur secondary to viral infections or when the sinuses become blocked. Properly treating initial viral infections and promptly addressing symptoms of bacterial infection can help prevent the progression to sinusitis.
Anatomical Factors: Structural issues like deviated septum, nasal polyps, or narrow sinus openings can contribute to chronic sinusitis. Consultation with an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist can help identify these anatomical factors and determine appropriate treatment options.
Management of Triggers:
Maintain Nasal Health: Keeping the nasal passages moist and clear can help prevent sinusitis. Nasal saline rinses or sprays can help flush out irritants, allergens, and excess mucus, reducing inflammation and preventing infections.
Allergen Management: Avoiding allergens is paramount for preventing allergic reactions that can lead to sinusitis. Implement measures such as using allergen-proof bedding, keeping windows closed during high pollen seasons, and maintaining clean indoor spaces to reduce allergen exposure.
Humidification: Maintaining optimal indoor humidity levels (around 40-50%) can help prevent excessive drying of the nasal passages, reducing the risk of sinus irritation. Use humidifiers or dehumidifiers as needed to achieve this balance.
Avoid Irritants: Steer clear of tobacco smoke, strong perfumes, and other environmental irritants that can trigger or worsen sinusitis symptoms. If you smoke, quitting can significantly improve sinus health.
Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity helps boost the immune system and improves circulation, which can aid in preventing sinus infections.
Balanced Diet: Consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins provides essential nutrients that support immune function and overall health.
Hydration: Staying well-hydrated thins mucus secretions, making it easier for the sinuses to drain properly and reducing the risk of congestion.
Proper Hand Hygiene: Washing hands frequently, especially during cold and flu seasons, can prevent the spread of viruses that contribute to sinusitis.
Prompt Treatment: If symptoms of a cold or upper respiratory infection persist, consult a healthcare professional for appropriate treatment. Treating these infections promptly can help prevent their progression to sinusitis.
Consultation with Specialists: If you experience chronic or recurrent sinusitis, seek the expertise of an ENT specialist. They can evaluate for anatomical issues, nasal polyps, and other factors that might be contributing to your condition.
In conclusion, the identification and management of triggers play a crucial role in preventing and managing sinusitis. By understanding the factors that contribute to sinus inflammation and implementing proactive measures, individuals can reduce the frequency and severity of sinus infections. Incorporating a combination of environmental adjustments, hygiene practices, and medical guidance can lead to better sinus health and an improved quality of life.
. ,
Book an Appointment